 | The Autonomic Nervous System |  |
 | The Autonomic Nervous System |  |
 The
organs (the "viscera") of our body, such as the heart, stomach and
intestines, are regulated by a part of the nervous system called the autonomic nervous system (ANS). The ANS is part of the
peripheral nervous system and it controls many organs and muscles within
the body. In most situations, we are unaware of the workings of the ANS
because it functions in an involuntary, reflexive manner. For example, we
do not notice when blood vessels change size or when our heart beats
faster. However, some people can be trained to control some functions of
the ANS such as heart rate or blood pressure. The
organs (the "viscera") of our body, such as the heart, stomach and
intestines, are regulated by a part of the nervous system called the autonomic nervous system (ANS). The ANS is part of the
peripheral nervous system and it controls many organs and muscles within
the body. In most situations, we are unaware of the workings of the ANS
because it functions in an involuntary, reflexive manner. For example, we
do not notice when blood vessels change size or when our heart beats
faster. However, some people can be trained to control some functions of
the ANS such as heart rate or blood pressure. The ANS is most important in two situations:
|
The ANS regulates:
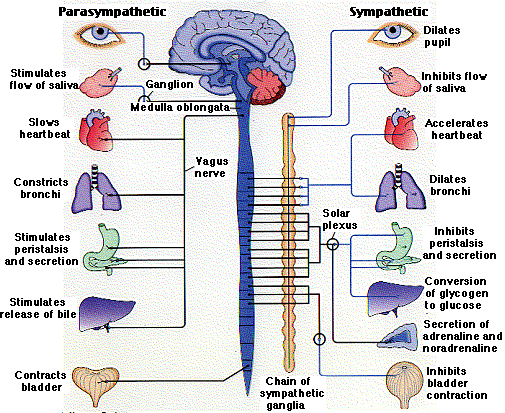
The ANS is divided into three parts:
|
|
|
| The Autonomic Nervous System | ||
| Structure | Sympathetic Stimulation | Parasympathetic Stimulation |
|---|---|---|
| Iris (eye muscle) | Pupil Dilation | Pupil Constriction |
| Salivary Glands | Saliva production reduced | Saliva production increased |
| Oral/Nasal Mucosa | Mucus production reduced | Mucus production increased |
| Heart | Heart rate and force increased | Heart rate and force decreased |
| Lung | Bronchial muscle relaxed | Bronchial muscle contracted |
| Stomach | Peristalsis reduced | Gastric juice secreted; motility increased |
| Small Intestine | Motility reduced | Digestion increased |
| Large Intestine | Motility reduced | Secretions and motility increased |
| Liver |
Increased conversion
of glycogen to glucose | |
| Kidney | Decreased urine secretion | Increased urine secretion |
| Adrenal medulla | Norepinephrine and epinephrine secreted | |
| Bladder |
Wall relaxed Sphincter closed | Wall contracted Sphincter relaxed |
| It should be noted that the autonomic
nervous system is always working. It is NOT only active during "fight or
flight" or "rest and digest" situations. Rather, the autonomic nervous
system acts to maintain normal internal functions and works with the somatic
nervous system. The enteric nervous system is a third division of the autonomic nervous system that you do not hear much about. The enteric nervous system is a meshwork of nerve fibers that innervate the viscera (gastrointestinal tract, pancreas, and gall bladder). |
|
|
|
|
| Actions of the Autonomic Nervous System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Effector Organ | Autonomic Division | Action |
| Eye : pupil | sympathetic
parasympathetic |
dilation of the pupil
constriction of the pupil |
| Eye : ciliary muscle | sympathetic
parasympathetic |
allows far vision
allows near vision |
| Lachrymal (tear) glands | sympathetic
parasympathetic |
vasoconstriction
secretion of tears |
| Salivary glands | sympathetic
parasympathetic |
vasoconstriction and secretion of mucous
with a low enzyme count
secretion of watery saliva with a high enzyme count |
| Heart | sympathetic parasympathetic |
dilation of coronary arteries, increased
heart rate, increased force of contraction, increased rate of pacemaker
conduction
coronary artery constriction slows, heart rate, reduces contraction and conduction, constricts coronary arteries |
| Bronchii | sympathetic
parasympathetic |
dilation
constriction and mucous secretion |
| Oesophagus | sympathetic
parasympathetic |
vasoconstriction
peristalsis, secretion of mucous |
| Stomach and Intestines | sympathetic parasympathetic |
inhibition of peristalsis and secretion
vasoconstriction, spinctre contraction peristalsis and secretion |
| Spleen | sympathetic | contraction |
| Adrenal medulla | sympathetic | adrenaline and noradrenaline secreted into the bloodstream |
| Liver | sympathetic | break down of glycogen (glyogenolysis) |
| Gall Bladder | sympathetic
parasympathetic |
relaxation
contraction |
| Pancreas | sympathetic | inhibition of insulin secretion
stimulation of insulin secretion |
| Descending colon | sympathetic parasympathetic |
vasoconstriction
inhibition of peristalsis and secretion peristalsis and secretion |
| Sigmoid colon, rectum and anus | sympathetic parasympathetic |
constriction of sphincter muscles
inhibition of peristalsis and secretion peristalsis and secretion |
| Bladder | sympathetic parasympathetic |
contraction of sphincter
relaxation of detrusor muscle contraction of detrusor muscle |
| Penis | sympathetic
parasympathetic |
ejaculation
erection |
| Clitoris | parasympathetic | erection |
| Uterus | sympathetic | contraction
relaxation |
| Blood vessels in: | ||
| Skin | sympathetic | constriction |
| Mucosal linings | sympathetic | constriction |
| Muscle | sympathetic | dilation |
| Kidneys | sympathetic | constriction |
| Lungs | sympathetic | constriction |
| Intracranial | sympathetic | slight constriction |
| Sweat glands | ||
| sweat glands except palm of hands | sympathetic | sweating |
| sweat glands on palms of hands | sympathetic | sweating |
| Pilomotor muscles at root of body hair | sympathetic | piloerection (making hair "stand on end") horripilation ("goose pimples") |
| Adipose tissue | sympathetic | lipolysis (break down of fat to release energy) |
| Try It!
| Interactive Word Search Puzzle on the Autonomic Nervous System |
More on the autonomic nervous system:
|
| BACK TO A&P 2 LAB #2 |